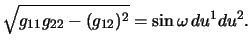7. Assume that
![]() is a surface whose
principal curvatures
is a surface whose
principal curvatures ![]() and
and ![]() satisfy
satisfy
![]() and
and
![]() at all points in
at all points in ![]() Let
Let
![]() be the unit normal and let
be the unit normal and let
![]() be principal curvature coordinates.
Show that the functions
be principal curvature coordinates.
Show that the functions
8. Let
![]() be a surface in
be a surface in ![]() with constant Gauss curvature
with constant Gauss curvature ![]() defined in
asymptotic coordinates, and
parametrized by arc length so that
defined in
asymptotic coordinates, and
parametrized by arc length so that
a) Show that
![]() satisfies the differential equation
satisfies the differential equation
Hint: Use Gauss' equation which in the coordinates of the
problem is
![\begin{displaymath}K = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{1-(g_{12})^2}}\left[
\frac{\partial}{\par...
...^2}}\left ( \frac{g_{12,1}}{\sqrt{1-(g_{12})^2}}\right)\right] \end{displaymath}](img25.gif)
b) Show that every polygon ![]() with four sides and which is bounded by
parameter curves has the area
with four sides and which is bounded by
parameter curves has the area
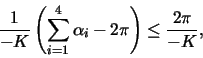
Hint: The area element is